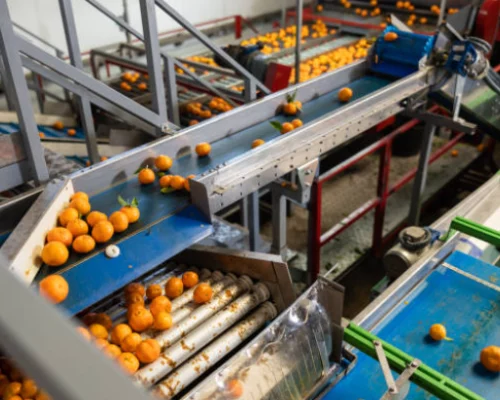
The food sector is a large manufacturing industry that must meet special requirements, as the products they process are foods that are eventually ingested by people, so the brushes used in it must meet specific criteria.
To ensure that the industrial food process is safe, companies in the food sector must have processes that comply with a series of conditions set by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Brush manufacturers, as their products are widely used in various processes in food factories, must also adhere to FDA regulations to supply brushes certified as compatible with the food industry.
When a person accustomed to visiting industrial companies observes a food factory, the unique characteristics of these industries are quickly identified: machines made of stainless steel, technical plastics, hygiene and cleaning procedures, protection and control equipment to prevent cross-contamination, equipment to avoid contamination from human organic residues such as saliva or hair, and much more.
The FDA requires that the components of the machines (including technical brushes) use very specific materials that are stable when in contact with food, preventing contaminants from passing into the products.
Brush manufacturers, who primarily use plastic components, must ensure that:
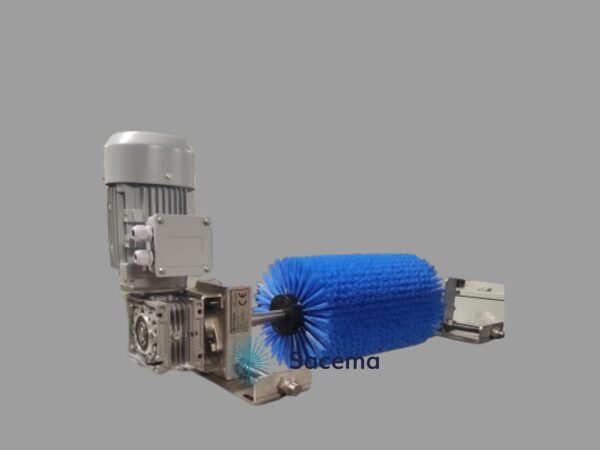
- The bases of the brushes must be made of virgin polyethylene, at least PE-300, and the use of plastics more susceptible to contamination such as polypropylene or PVC is not permitted. Normal rubber bases, standard 3D-printed PLA, and other complementary materials used on occasion must also be discarded.
- The brush filaments must not be made of polypropylene or PVC; some varieties of polyamides, and especially PBT, can be used.
- The staples that fix the brush tufts, being metallic, must also be stainless steel, with a minimum quality of 304. This is very important, as standard and easily obtainable staples are made of zinc-plated carbon steel, which are not allowed due to the risk of oxidation.
- The lubrication oil in the machine must be compatible with the FDA industry. This is another crucial point, as brush components like filaments or staples pass through permanently lubricated areas, so this lubrication oil must be FDA compatible.
- Natural filaments, whether of animal origin such as pig bristles or horsehair, or of vegetable origin such as tampico, are not compatible with this standard.
- Metal wire filaments can only be made of stainless steel, prohibiting the use of carbon steel, whether coated or uncoated, and brass.
- Similarly, fixing screws, shafts, pins, or any other commercial element used to attach the brush to the carrier machine must be made of stainless steel.
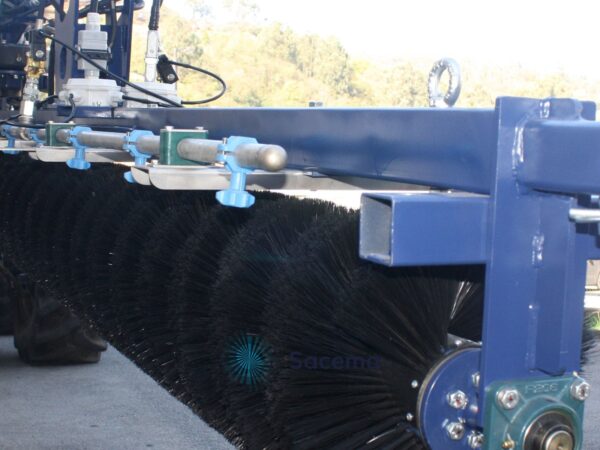
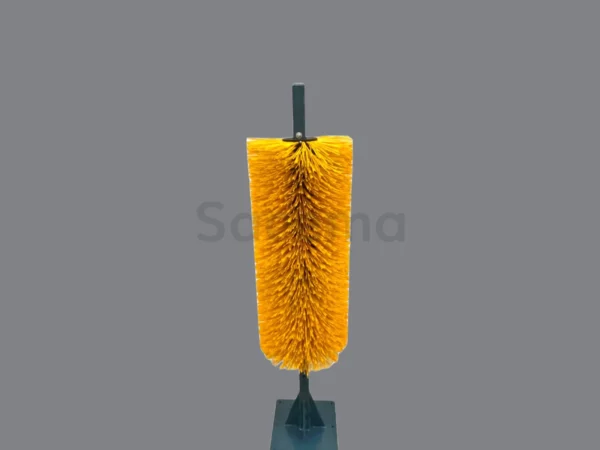
An important issue is the colour of the filaments. A technical brush has a risk of losing filaments, so the filaments must have a special colour that allows them to be visually detected if any unit comes loose and contaminates the food.
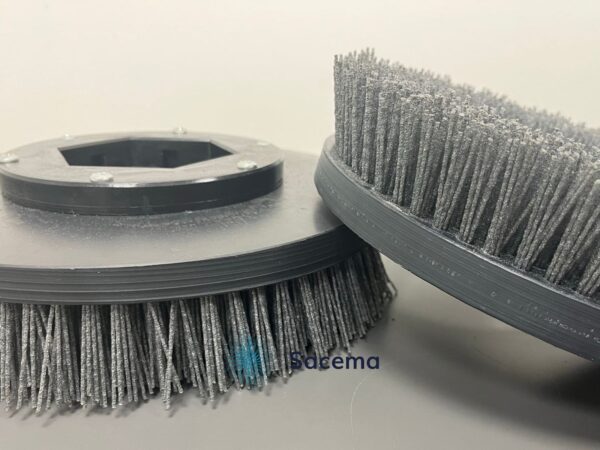
The typical, most used and common colour is the dark blue of special FDA PBT, which is mainly available in sizes 0.5 and 0.7 mm.
There is also a variety of PBT, also FDA compatible, called “metal detectable”. In its composition, it has a metallic charge, giving it a characteristic dark grey anthracite colour, which, available in 0.35 and 0.60 mm, can be detected in a metal detector incorporated into the process. The amount of filaments detected according to the detector’s own sensitivity must be checked.
Along with these brushes, a certificate of compatibility with the food industry is issued, specifying all the materials used in the manufacture of industrial technical brushes.
If you need any clarification about brushes in the food industry, do not hesitate to contact us.